Taxi sign and corresponding app¶
As an example resource, a taxi sign service has been created. It is one rather naive example of what could be added to a passenger car and would benefit from having a user interface in the infotainment head unit.
This taxi sign resource is a graphical application for running on Ubuntu, and will show a taxi sign lit up or turned off. The resource can also be used in command-line only mode (for use on Linux machines without graphics) or even connected to a real taxi sign with a light bulb. See below how to build your own taxi sign hardware controlled by a Beaglebone!
Taxi sign resource¶
Minimum Python 3.3 should be used for this software to run properly.
To find usage information on this (and other scripts mentioned in this section), use the -h command line switch:
$ python3 examples/taxisignservice/taxisignservice.py -h
The taxi sign service listens to this command:
command/taxisignservice/state True
and it will respond on the corresponding data topic.
To test the taxisign resource, run this in three different terminal windows:
$ mosquitto_sub -t +/# -v
$ python3 examples/taxisignservice/taxisignservice.py -v -mode graphical
$ mosquitto_pub -t command/taxisignservice/state -m True
The last command will turn on the taxi sign. Using ‘False’ as payload will turn it off. This is how the taxi sign looks like when on, and off (and in addition disconnected from the broker) respectively:


As seen in the mosquitto_sub window, also availability data is sent upon startup:
resourceavailable/taxisignservice/presence True
commandavailable/taxisignservice/state True
dataavailable/taxisignservice/state True
data/taxisignservice/state False
Kill the taxisignservice process to see the last will being sent from the broker.
The service manager will send out the presence information for the individual signals.
Try it using:
$ ps -ef
$ kill <PID for taxisignservice>
Taxi sign application¶
The taxi sign app (application) is a graphical program that is turning on or off the taxi sign (simulated or real hardware). The taxi sign app can also be used in command-line only mode (for use on Linux machines without graphics).
First test the taxi sign app standalone, with a broker only (make sure the broker is running). Start the taxi sign app in graphical mode:
$ python3 examples/taxisignapp/taxisignapp.py -mode graphical
In a separate terminal window, send information to the taxi sign app that the taxi sign resource is online and that the sign is lit up:
$ mosquitto_pub -t resourceavailable/taxisignservice/presence -m True
$ mosquitto_pub -t data/taxisignservice/state -m True
In yet another terminal window, listen to all MQTT commands:
$ mosquitto_sub -t +/# -v
Then press the buttons on the taxi sign app. It will show something like this:
command/taxisignservice/state True
command/taxisignservice/state False
This is how the taxi sign app looks like, when the taxi sign is on, and when the taxi sign is disconnected from the broker:
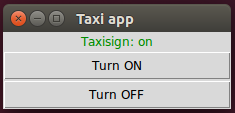
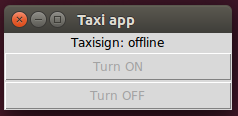
Now it is time to test the taxi sign app and the taxi sign resource together. Run these in separate terminal windows:
$ python3 examples/taxisignapp/taxisignapp.py -v -mode graphical
$ python3 examples/taxisignservice/taxisignservice.py -v -mode graphical
Try for example to kill the broker and then start it again.
Help texts for the taxi sign resource and app¶
Details of usage for the taxi sign related examples are found here:
$ python3 examples/taxisignservice/taxisignservice.py -h
usage: taxisignservice.py [-h] [-v] [-host HOST] [-port PORT] [-cert CERT]
[-mode {hardware,commandline,graphical}]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-v Increase verbosity level. Can be repeated.
-host HOST Broker host name. Defaults to localhost.
-port PORT Broker port number. Defaults to 1883.
-cert CERT Directory for certificate files. Defaults to not using
certificates.
-mode {hardware,commandline,graphical}
Type of simulator to use. Depends on graphical display
or taxi sign hardware. Defaults to 'commandline'.
A taxi sign service example for the Secure Gateway concept architecture.
This is a "Resource" according to the Secure Gateway nomenclature. It registers on
the Secure Gateway network, and accepts commands to turn on or off a
hardware taxi sign. It is intended for running on Beaglebone with appropriate
electronics connected to a GPIO output pin to contol the taxi sign. Note that
root/sudo permissions typically are required to control GPIO pins.
This resource sends out on start-up:
resourceavailable/taxisignservice/presence True
commandavailable/taxisignservice/state True
datavailable/taxisignservice/state True
This resource is listening for:
command/taxisignservice/state True/False
This resource sends out on state change:
data/taxisignservice/state True/False
It can also be used in two different simulation modes. This is handy when no
taxisign hardware is available (or no sudo/root permission is available). The
command line mode simulator should always be available. The graphical mode
simulator requires Tk installed on the machine. This is typically installed with:
sudo apt-get install python3-tk
This resource can connect to the broker in a secure or insecure way. The settings
of the broker determines what is allowed. To connect in the secure way,
the directory of the certificate files must be specified.
The certificate files should be named:
CA file: ca_public_certificate.pem
Certificate file: public_certificate.pem
Key file: private_key.pem
$ python3 examples/taxisignapp/taxisignapp.py -h
usage: taxisignapp.py [-h] [-v] [-host HOST] [-port PORT] [-cert CERT]
[-mode {commandline,graphical}]
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-v Increase verbosity level. Can be repeated.
-host HOST Broker host name. Defaults to localhost.
-port PORT Broker port number. Defaults to 1883.
-cert CERT Directory for certificate files. Defaults to not using
certificates.
-mode {commandline,graphical}
Type of use interface. Depends on graphical display.
Defaults to 'commandline'.
A taxi sign app example for the Secure Gateway concept architecture.
This is an "App" according to the Secure Gateway nomenclature. It registers on
the Secure Gateway network, and sends commands to turn on or off a hardware
taxi sign (or a simulated sign).
The corresponding taxisign resource must be online. This app listens for:
resourceavailable/taxisignservice/presence True
This app is sending:
command/taxisignservice/state True
This app is receiving:
data/taxisignservice/state True
It can be used in two different modes. The command line mode should always
be available. The graphical mode requires Tk installed on the machine.
This is typically installed with:
sudo apt-get install python3-tk
This app can connect to the broker in a secure or insecure way. The settings
of the broker determines what is allowed. To connect in the secure way,
the directory of the certificate files must be specified.
The certificate files should be named:
CA file: ca_public_certificate.pem
Certificate file: public_certificate.pem
Key file: private_key.pem
Build your own Secure Gateway enabled taxi sign hardware¶
The taxisignservice resource software is handling turning on and off a digital output pin on a BeagleBone or Raspberry Pi embedded Linux computer board. Use the command:
$ sudo python3 taxisignservice.py -v -mode hardware -host 192.168.0.93
Replace the IP number with your broker’s IP number. Due to the hardware manipulation on the Beaglebone/Pi, you must run the program in ‘sudo’ mode.
Connect the output GPIO pin to a relay driver. The GPIO pin number to use is defined in the taxisigndriver file, and there is also more technical information in that file. A power supply and a lightbulb are connected to the relay. Cheap taxi sign fixtures are available on several of the common low-price marketplaces on the Internet.
Set the broker IP number manually when starting the taxisignservice, or write a small startscript that uses Avahi to find the broker IP number.
To test the GPIO output driver:
$ sudo python3 examples/taxisignservice/drivers/taxisign_driver.py